SUMMARY:
• Cantilever based biosensors are a very common type of microsensor
• They are relatively easy to produce and use
• Microdispensing is very useful to activate their surface and functionalize it with different biomolecules
Background
Over the past decades, microcantilever biosensors have demonstrated exceptional capabilities for detecting biomolecules in liquid environments. These sensors operate label-free, meaning they do not require chemical tags, and they can deliver real-time results.
Using multiple cantilevers on a single chip offers several key advantages:
- Internal controls to reduce false positives
- Differential readouts to correct for environmental drift
- Parallel sensing of different analytes or surface chemistries
This multi-cantilever approach enhances reliability and enables more sophisticated biosensing strategies. They have been successfully used for e.g. printing Bacteria and sensing biomolecules [1][2].
The images and videos used here originate from research of Prof. Hegner’s group at Trinity College Dublin. You can learn more about their work on their website.
Reasons for Using Inkjet Printing
Microdispensing offers several advantages:
-
Faster functionalization process.
-
Minimizes liquid volumes, conserving reagents.
-
Dispensing on both sides of the sensor structure without turning, as shown in the video blow.
-
No manual alignment is required—the Autodrop Gantry’s positioning accuracy of below 1 µm significantly reduces setup complexity.
-
Rapid creation of dispensing patterns on target surfaces.
-
Contact free dispensing supports both static and dynamic mode sensing, which are sensitive to:
-
Surface stress
-
Receptor layer distribution
-
Analyte binding locations
-
-
Scalable to large cantilever arrays.
-
Non-contact coating of arbitrary structures.
Fabrication Process
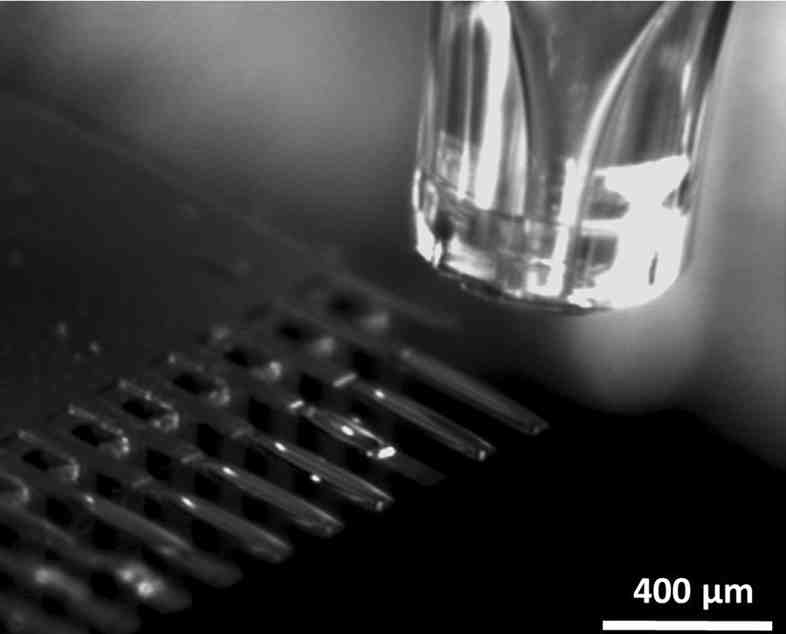
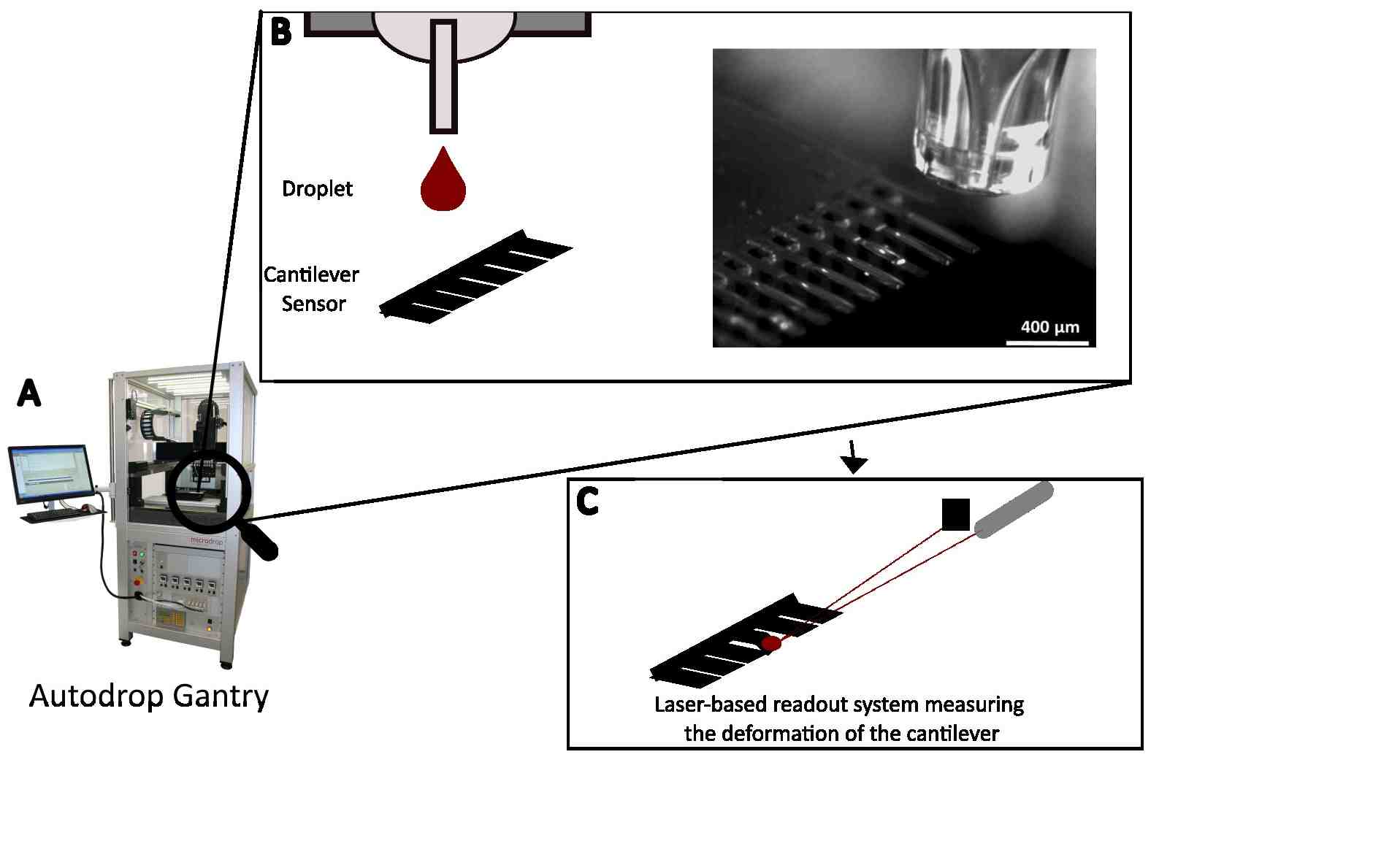
Cantilever sensors can be functionalized using a piezo-driven inkjet dispensing system that precisely deposits picoliter droplets onto one side of each cantilever, forming a coating layer. The process can be automated, is fast, and scalable, and with environmental controls for humidity and temperature to ensure consistent droplet formation and solution stability.
The cantilever based sensor can then be used for instance in a laser-based readout system to study the effect of different biomolecules.
Utility and Outlook
Activating the surface of cantilever sensors via microdispensing offers scalability, automation, and multimodal sensing capabilities, positioning the platform as a powerful tool for advanced biosensing applications. Future improvements may focus on enabling dual-side functionalization, expanding multiplexing strategies, and integrating enhanced environmental controls to boost reliability and adaptability in clinical and research settings.
Coating of Cantilever Sensors in Action
References
- We are grateful to Prof Hegner and his group for allowing us to use their images and videos. Their website can be found here http://www.tcd.ie/Physics/people/martin-hegner/
- Further references include: