Background
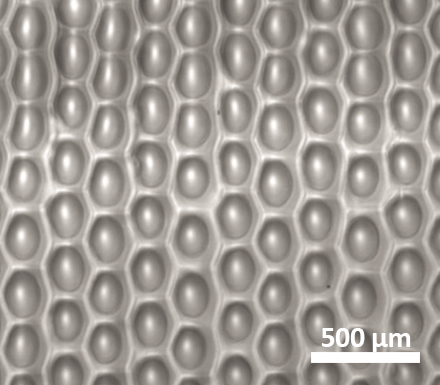
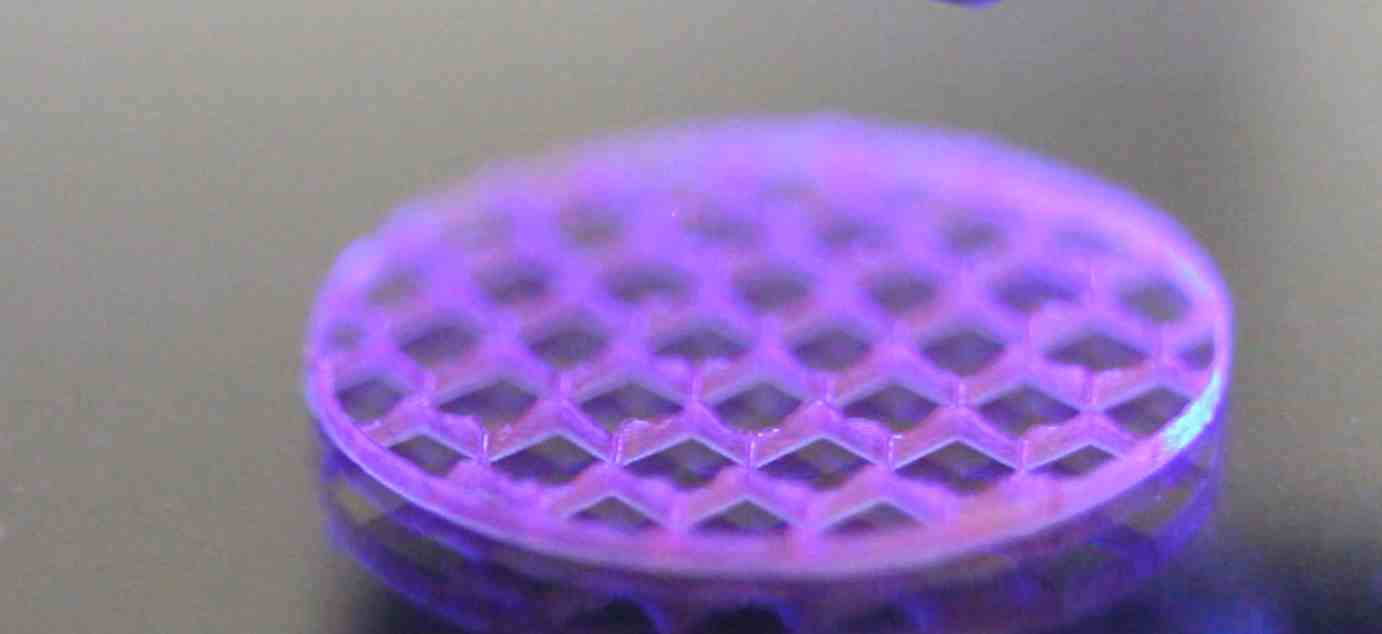
Bioprinting builds on traditional 3D printing techniques by using living biomaterials to dispense structures such as scaffolds, drugs, and individual cells. This technology holds great promise for advancing regenerative medicine, minimizing animal testing, and enabling personalized drug testing through organoids and organ-on-a-chip systems. Microdispensing plays a key role in this context, as it allows for the precise delivery of extremely small volumes—ideal for creating intricate, minuscule biological structures.
Just getting started with 3D Bioprinting? Read more about Bioprinting in this comprehensive article here.
Challenges
- Bioprinting is highly versatile, requiring precise coordination between scaffolds and cells, as well as accurate placement of diverse cell types.
- Environmental control is critical especially since living cells are extremely sensitive to factors like temperature, pH, oxygen levels, nutrients, and mechanical forces—any fluctuation can compromise cell viability and tissue formation.
Your Advantages of Using Microdispensing
-
Microdispensing is very versatile- it can handle different cell types as well as different scaffolding materials, like hydrogels.
- Microdrop’s Autodrop Gantry II system offers precise monitoring and positioning of the dispensing process.
- Using different Addons parameters like temperature, humidity, and pressure can be controlled, supporting the viability of cells and the success of bioprinting processes.
Example Applications of Microdispening in Bioprinting
- Dispensing Single Cells
- Dispensing Hydrogels
Use Cases for Bioprinting
Microdrop-Clients & References

"I can say that I am very satisfied with microdrop. Their services and products have exceeded my expectations"
Prof. Dr. Dr. Gernot Teichmann